Foods High in Omega-3 Fatty Acids
Foods high in omega-3 fatty acids should be included in your diet to help lower inflammation and prevent many chronic diseases. But what foods contain omega-3 fatty acids? What are the different types of omega-3 fatty acids? Why are they important in your body? How much do you need?
Every month I highlight a nutrient you should know about. This month we’re focusing on OMEGA-3 FATTY ACIDS as a nutrient of concern…

Omega-3 fatty acids are an essential nutrient to consume. Your body cannot produce them, so you must obtain them from your diet. There are three important types of omega-3 fatty acids: ALA (Alpha-Linolenic acid), DHA (Docosahexaenoic acid), and EPA (Eicosapentaenoic acid). ALA is found mostly in plants, while DHA and EPA which are found both mostly in animal foods and algae. All three types of omega-3 fatty acids are important for your overall health and well-being.
Types of Omega-3 Fatty Acids
Omega-3 fatty acids are polyunsaturated fats. That means they have more than one double bond in their chemical structure. Unsaturated fats are heart-healthy fats.
There are three types of omega-3 fatty acids:
ALA (Alpha-Linolenic acid)
ALA is the most common omega-3 fatty acid in your diet. It’s found in a wide range of plant foods, including nuts and seeds, soybean oil, canola oil, and some vegetables.
To be used in your body, ALA must first be converted to DHA and EPA. When you consume ALA, your body needs to do work before utilizing it, but unfortunately only a small amount of the ALA you consume is actually converted to DHA and EPA. No, it’s not the most efficient system, which is why consuming DHA and EPA are so important.
DHA (Docosahexaenoic acid) & EPA (Eicosapentaenoic acid)
DHA and EPA are found in animal-based fats, most notably fatty fish and fish oil. This is why you constantly hear about fish oil as the most potent source of omega-3 fatty acids. Upon consumption, your body can efficiently use DHA and EPA immediately, without converting them to another form (like your body must do with ALA).
EPA is found in fatty fish and fish oil and has several functions in your body. Part of EPA can be converted to the most active omega-3 in your body, DHA.
DHA has key structural components in your body, making it the most important omega-3 fatty acid. It can be found in many animal products, including fish and fish oil, but also meat, eggs, and dairy from grass-fed animals.
What do Omega-3 fatty acids do in your body?
Omega-3 fatty acids have several important roles in your body, including:
- Structural component of retina (in your eyes) and cell membranes (especially DHA)
- Supports brain health and development during pregnancy, in babies and infants
- Reduces blood clots
- Reduce production of inflammatory molecules in your body, like eicosanoids and cytokines
- Promotes heart health by lowering triglycerides, reducing blood pressure, raising HDL (“good”) cholesterol levels, and preventing plaque buildup in arteries
- Increases insulin sensitivity, especially important for individuals with metabolic disorders, like type 2 diabetes
Omega-3 Fatty Acids vs. Omega-6 Fatty Acids
Omega-3 fatty acids and omega-6 fatty acids are both essential polyunsaturated fats. They have many overlapping roles in the body, including participating in inflammation and blood clotting.
Omega-6 fatty acids, however, can be pro-inflammatory, whereas omega-3 fatty acids are more anti-inflammatory. Some inflammation protects your body, but high levels of chronic inflammation can be detrimental to your health, driving the development of chronic diseases like heart disease, diabetes, Alzheimer’s disease, cancer and more.
Many typical “Western” diets are rich in omega-6 fatty acids, but low in omega-3 fatty acids. Researchers have found that having a high omega-6 to omega-3 ratio in your diet can actually promote inflammation. Our ancestors typically had an omega-6:omega-3 ratio ranging from 4:1 to 1:4, but today it is estimated that consumption ratios are up to 16:1!
It is essential to balance the quantity of omega-3 and omega-6 fatty acids you consume, by eating more omega-3-rich foods and less omega-6 heavy foods.
Foods rich in omega-6 fatty acids include highly processed vegetable and seed oils. Soybean oil is currently the greatest source of omega-6 fatty acids in America because it’s widely used in many highly processed and packaged foods.
Read on to learn the foods high in omega-3 fatty acids…
How much omega-3 fatty acids do you need?
The reference daily intake (RDI) of combined EPA and DHA is 250-500 mg. The combined total for ALA, EPA, and DHA for women is 1,100 mg and for men 1,600 mg.
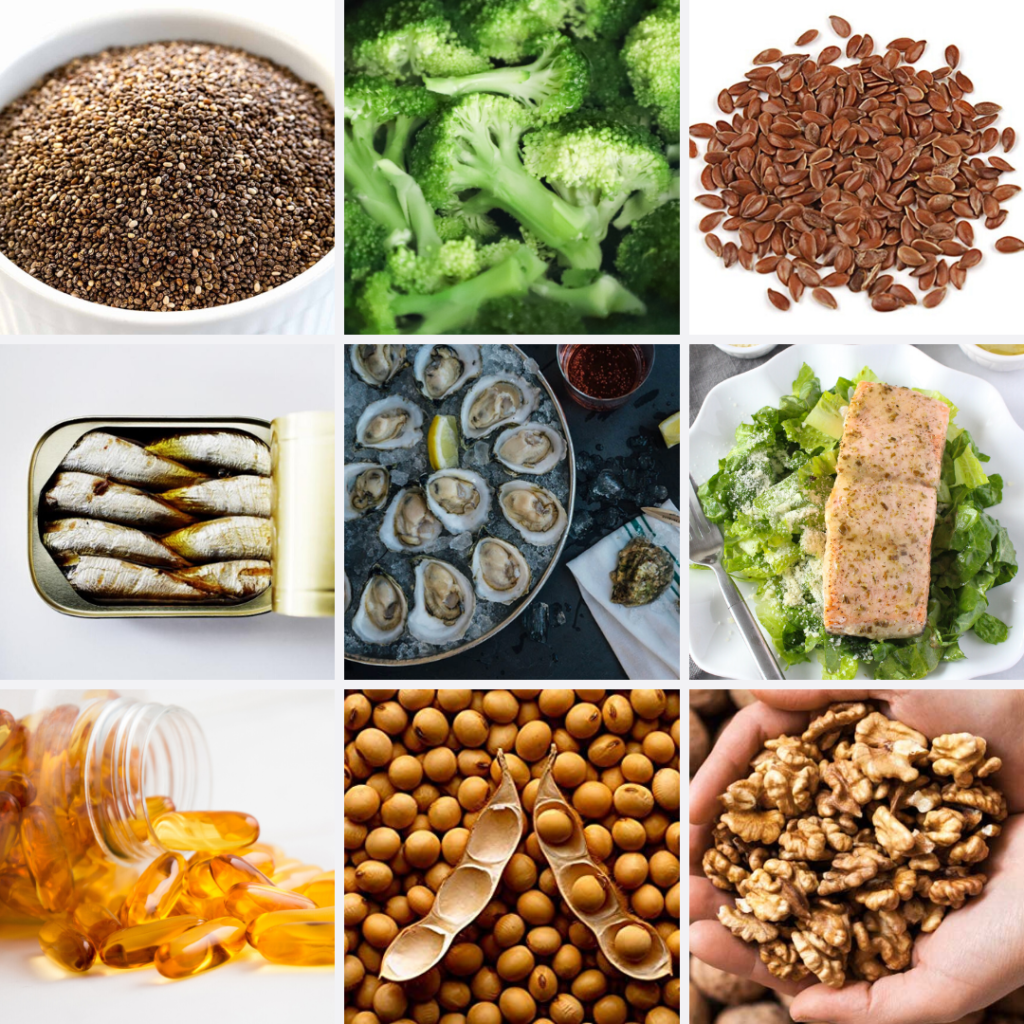
Foods High In Omega-3 Fatty Acids:
Plant-rich foods high in ALA:
- Flaxseed
- Chia seed
- Hemp seed
- Walnuts
- Edamame
- Plant oils (ie: canola oil)
- Brussel sprouts
- Broccoli
- Spinach
- Kale
- Wild rice
Foods high in EPA/DHA:
- Salmon
- Mackerel
- Tuna
- Sardines
- Herring
- Cod liver oil
- Anchovies
- Oysters
- Shrimp
- Seaweed/Algae
- Pasture-raised eggs

What recipes contain foods high in omega-3 fatty acids?
Plant-based recipes rich in ALA omega-3 fatty acids:
- Chia pudding (chia seeds)
- Peach Pie Protein Pancakes (contain flaxseeds and chia seeds)
- Spinach and Artichoke Frittata (spinach)
- Wild Rice Stuffing (wild rice)
- Broccoli and Apple Salad (broccoli)
- Crispy Roasted Edamame (soybeans)
Recipes rich in EPA and DHA omega-3 fatty acids:
- Mediterranean Salmon Salad (salmon)
- Salmon Nicoise Salad (salmon)
- Tuna Avocado Salad (tuna)
- 2-Ingredient Egg Muffins (if use pasture-raised eggs)
- 10-Minute Salmon
What are the health benefits of omega-3 fatty acids?
Omega-3 fatty acids contribute to many benefits in your body:
Fights Inflammation
The cornerstone role of omega-3 fatty acids in fighting inflammation is what contributes to their variety of health benefits. Omega-3 fatty acids interfere with the production of inflammatory molecules in your body.
Lowers your risk of heart disease
Evidence is clear that high omega-3 fatty acid intake is associated with lower triglycerides (fats in your blood), which lowers your risk of heart diseases, including stroke, heart attack, and more. Furthermore, omega-3 fatty acids can also help reduce blood pressure, raise “good” HDL cholesterol levels while lowering “bad” LDL cholesterol levels, and help prevent plaque build up.
Fights depression and anxiety
Studies indicate that individuals who consume omega-3 fatty acids on a daily basis are less likely to experience symptoms of depression. High omega-3 intake can also help improve depressive and anxious symptoms.
Improves eye health
Consuming enough omega-3 fatty acids have been shown to decrease risk of macular degeneration, cataracts, glaucoma, and blurry vision.
Supports a healthy, full-term pregnancy
Sufficient DHA can reduce the risk of preterm birth by 42%! Researchers at Harvard discovered that low omega-3 fatty acid blood levels were associated with significantly higher rates of early preterm birth (before 34 weeks gestation). Most pregnant women don’t consume enough DHA to lower preterm birth risk. Only 1 in 10 pregnant and nursing women report taking a supplement. Learn more about the importance of omega-3 fatty acids during pregnancy here.
Promotes fetus brain development during pregnancy
High omega-3 fatty acid intake during pregnancy and after promotes higher intelligence, better communication and social skills, fewer behavioral problems, and decreased risk of ADHD and autism for your baby.
Fights age-related mental decline
Improve bone and joint health
Omega-3 fatty acid intake can improve bone strength by helping boost the amount of calcium in your bones. Other studies have reported omega-3 fatty acids can help reduce joint caused by arthritis.
Supports healthy skin
Omega-3 fatty acids are an important structural component of cell membranes. They contribute to your skin’s natural glow!
Should you supplement with omega-3 fatty acids?
Always consult with your physician or a registered dietitian before taking any supplement as it can interfere with some medications. If you don’t consume many foods high in omega-3 fatty acids mentioned above, it may be beneficial to supplement.
According to the American Pregnancy Association, a supplement that contains at least 300 mg DHA is highly recommended for healthy brain growth and development during pregnancy and during breastfeeding, but always check with your OB/midwife first.

And there you have it… a quick recap about the importance of omega-3 fatty acids in your diet, what foods contain omega-3 fatty acids, and if you should ask your doctor about supplementing!
Questions? I’d love to hear from you!
XO

 Hi there!
Thanks for stopping by! I'm Chelsey, an online Registered Dietitian, recipe developer, budding photographer, and coffee addict! My mission is to help you feel good through food by answering the question "What should I eat?" Let's make nutrition approachable!
I hope you enjoy my personal collection of simple, healthy, food allergy friendly and nutritiously delicious recipes, plus tips and tons of tricks that will help YOU live a nutritionally-balanced life! I look forward to getting to know you better...
Hi there!
Thanks for stopping by! I'm Chelsey, an online Registered Dietitian, recipe developer, budding photographer, and coffee addict! My mission is to help you feel good through food by answering the question "What should I eat?" Let's make nutrition approachable!
I hope you enjoy my personal collection of simple, healthy, food allergy friendly and nutritiously delicious recipes, plus tips and tons of tricks that will help YOU live a nutritionally-balanced life! I look forward to getting to know you better...







