What Foods Contain Potassium?
What foods contain potassium? Why is potassium important in your body? How much do you need? Every month I highlight a nutrient you should know about. This month we’re focusing on POTASSIUM as a nutrient of concern…

If you’re like most people in the U.S., you don’t eat enough potassium-rich foods. Potassium (K+) is an important mineral and electrolyte in your body, essential for muscle contraction, nerve conduction, blood pressure regulation, and much more. It’s so important, it’s the third most abundant mineral in your body.
Most Americans these days consume twice as much sodium compared to potassium – we want to flip that!
Since potassium is essential for so many organs in your body, it’s important to consult with a physician or dietitian before making changes to your diet or supplement routine. Individuals with heart conditions or kidney disease should especially consult with their physician.
What does potassium do in your body?
As a positive electrolyte, potassium is able to conduct electricity, which leads to its widespread roles in your body:
- Essential for muscle contraction, including your heart beat
- Regulates fluid balance, including water retention and swelling, acting as an electrolyte
- Sends nerve signals
- Wards against dehydration
- Prevents against kidney stones
- Keeps heartbeat regular
- Counter-balanced sodium
Where is potassium found in the body?
Most of the potassium in your body is found INSIDE your cells. Mostly found in your muscle cells, but also bone, liver, and red blood cells too.
How much potassium do you need?
The adequate intake (AI) for potassium in adults ages 19-50 is 3,400 mg for men 2,600 mg for women, although some reports estimate the AI to be up to 4,700 mg per day.
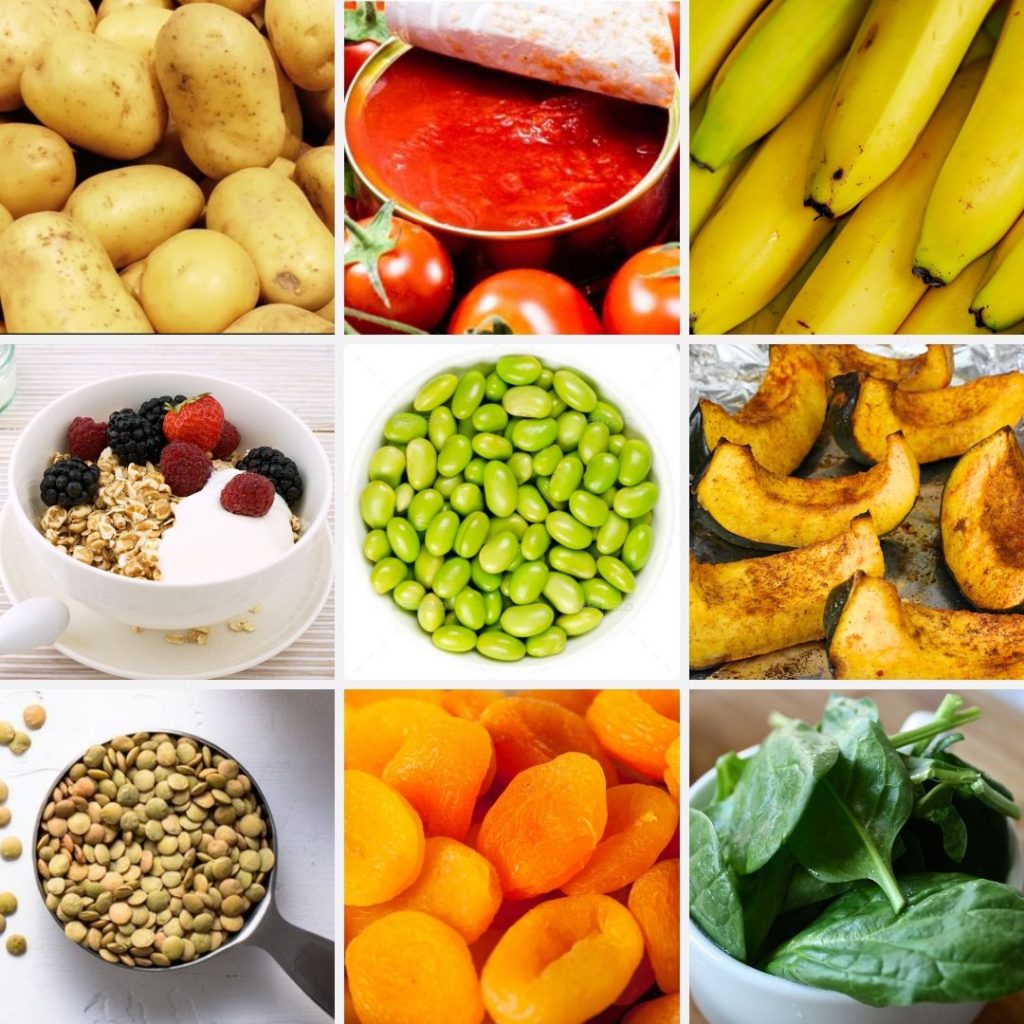
What foods contain potassium?
The best way to increase your potassium intake is to eat potassium-rich foods. Luckily, there are TONS of plant-based AND animal-based foods that are rich in potassium. P.S. – Even coffee contains some potassium!
Bananas get most of the hype of all the foods containing potassium, but there are TONS of other fruits and vegetables that are potassium-rich too.
The following foods contain potassium:
- Dried apricots, prunes, raisins
- Lentils and kidney beans
- Acorn squash
- Potatoes
- Soybeans
- Bananas
- Milk and yogurt
- Spinach
- Tomatoes
- Chicken
- and much, much more!

What recipes contain sources of potassium?
Try these recipes made with foods that contain potassium:
- Stuffed Acorn Squash
- Easy Lentil Tacos
- Tuna Nicoise Salad Stuffed Potatoes
- Crispy Roasted Edamame
- Simple Ratatouille
- Vegan Chili
- Banana Bread Overnight Oats
What are the health benefits of potassium?
Potassium contributes to many health benefits in your body:
Protects heart health and blood pressure
Potassium is February’s nutrient of the month because it’s also heart health month and potassium is vital for heart health! Potassium helps regulate blood pressure (counter-balancing sodium) and muscle contraction, so it’s essential for your heart health.
Low potassium intake increases the risk of high blood pressure, likely due to increased calcification and stiffness of your blood vessels. Increased potassium intake helps lower blood pressure by dilating arteries and increasing sodium excretion. These effects are especially pronounced in salt-sensitive individuals.
Prevents Kidney Stones
Potassium acts in the kidneys, impacting the reabsorption of other minerals, like calcium. Consistently low potassium intake impairs calcium reabsorption in the kidneys, which can increase the risk of kidney stones.
Protects Bone Health
Although the research is still extracting the exact mechanism of how potassium impacts bone health, increasing your intake of fruits and vegetables – specifically due to the increased potassium intake – has been shown to increase bone mineral density and help prevent osteoporosis.
Prevents Type 2 Diabetes
Potassium is required for proper insulin secretion, so low potassium diets could play a role in the development of type 2 diabetes.
Reduces Water Retention
Potassium counteracts sodium, so a diet high in potassium can help flush out excess water.
Do I need to supplement with potassium?
Since excessive potassium intake can be dangerous for your heart, kidneys, and overall health, it is best to consult with your physician or registered dietitian to determine if a supplement is needed.
By focusing on increasing your fruit and vegetable intake, you’ll easily increase your intake of potassium-rich foods.

And there you have it… a short recap about the importance of potassium in your diet, what foods contain potassium, and how to determine if a potassium supplement is right for you.
Questions? I’d love to hear from you!
XO
Important reminder: the information contained in this article is for EDUCATIONAL purposes only. ALWAYS consult with a physician or your registered dietitian before making drastic changes in your diet.

 Hi there!
Thanks for stopping by! I'm Chelsey, an online Registered Dietitian, recipe developer, budding photographer, and coffee addict! My mission is to help you feel good through food by answering the question "What should I eat?" Let's make nutrition approachable!
I hope you enjoy my personal collection of simple, healthy, food allergy friendly and nutritiously delicious recipes, plus tips and tons of tricks that will help YOU live a nutritionally-balanced life! I look forward to getting to know you better...
Hi there!
Thanks for stopping by! I'm Chelsey, an online Registered Dietitian, recipe developer, budding photographer, and coffee addict! My mission is to help you feel good through food by answering the question "What should I eat?" Let's make nutrition approachable!
I hope you enjoy my personal collection of simple, healthy, food allergy friendly and nutritiously delicious recipes, plus tips and tons of tricks that will help YOU live a nutritionally-balanced life! I look forward to getting to know you better...







